Causes and treatment of eye discharge in toddlers
Understanding and Treating Eye Discharge in Toddlers: What Parents Need to Know”
Eye discharge in toddlers can be concerning for parents, but understanding its causes and treatment options can provide peace of mind. From common colds to more serious infections, this article explores the symptoms, causes, and treatment of eye discharge in toddlers, along with when to seek medical help.
Symptoms of eye discharge in toddlers:
Eye discharge symptoms vary, but parents may notice:
- Eye pain
- Constant eye rubbing
- Reluctance to open the eye
- Eye swelling or facial swelling
- Red streaks around the eye
Causes of eye discharge in toddlers:
Eye discharge can result from various factors, including:
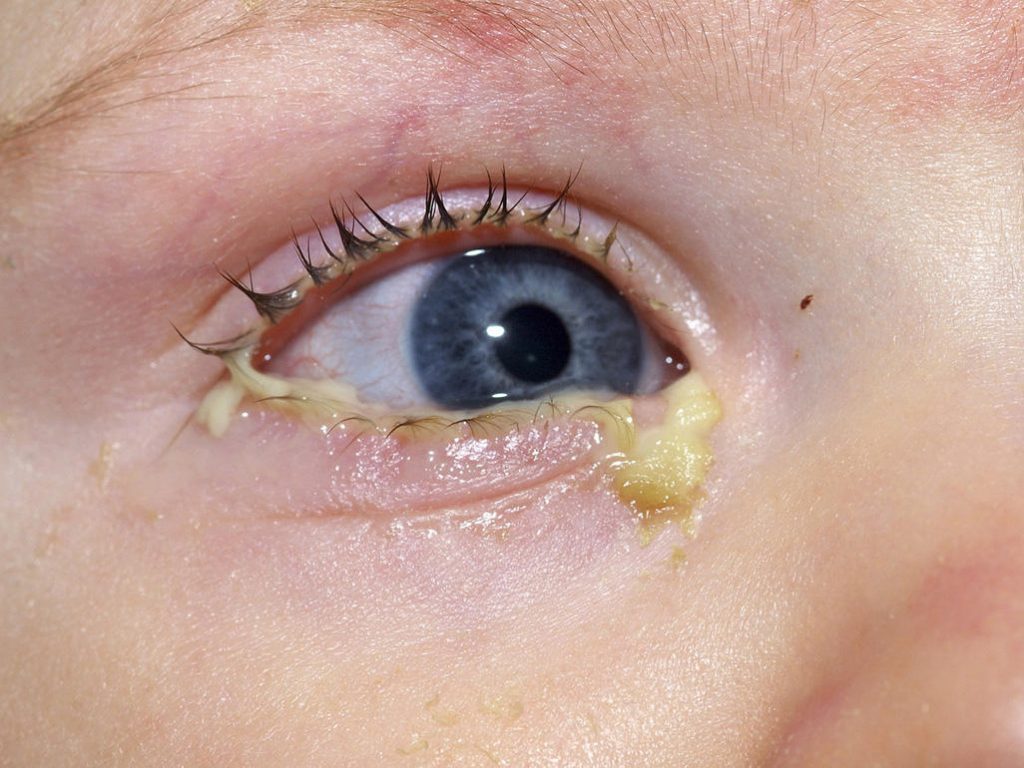
- Normal eye discharge: Usually harmless and may appear green, yellow, white, or clear.
- Pinkeye (conjunctivitis): Causes red, painful, inflamed eyes.
- Viral infection: Common cause of pinkeye, presenting with redness and swelling.
- Bacterial infection: Leads to sore, swollen eyes with green or yellow discharge.
- Blocked tear duct: Causes watery eyes, potential infection if red or irritated.
- Object in the eye: Foreign objects cause watering, irritation, and potential infection.
- Cellulitis: Serious infection causing painful, swollen eyes and fever.
- Stye: Painful, red lump from infected eyelid follicles, may ooze or cause discharge.
Treatment for eye discharge in toddlers:
Treatment depends on the cause and may include:
- Saline water irrigation for small objects, seeking medical help for larger ones.
- Warm compresses to ease symptoms of styes and blocked tear ducts.
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
- Steroids for viral infections or allergic reactions.
- Surgery for persistent blocked tear ducts.
Preventing eye discharge in toddlers:
Preventive measures include:
- Frequent handwashing to prevent infection spread.
- Discouraging eye rubbing.
- Avoiding lotions near the eyes.
- Maintaining eye and face cleanliness.
- Using eye protection during activities.
- Keeping toddlers with eye infections home from school.
When to see a doctor:
Seek medical attention if:
- Symptoms persist or worsen despite home treatment.
- Intense pain, swelling, or fever occurs.
- Eye cannot open, or there’s vision impairment.
- Severe redness or bleeding is present.
- Large object in the eye or symptoms of cellulitis arise.
FAQs:
Answers to common questions about eye discharge in toddlers:
- Morning eye stickiness may be due to discharge from colds, allergies, or infections.
- Yes, colds can cause eye discharge, as viral infections often accompany them.
- If eye discharge is excessive or persistent, consult a healthcare professional about school attendance.
Summary:
Eye discharge in toddlers is often manageable at home but may require medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen. Understanding the causes and seeking timely treatment can help ensure the well-being of your child’s eyes.
